
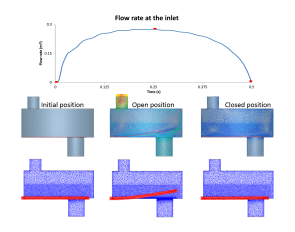
Nevertheless, it is known that the ALE-FSI approach guarantees more accurate results at the interface between the solid and the fluid.

The majority of the reported 3D heart valve FSI simulations are performed with the Eulerian formulation, allowing for large deformations of the domains without compromising the quality of the fluid grid. When setting up an FSI simulation, several choices have to be made to select the most suitable approach for the case of interest: in particular, to simulate flexible leaflet cardiac valves, the type of discretization of the fluid domain is crucial, which can be described with an ALE (Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian) or an Eulerian formulation. In recent years the role of FSI (fluid-structure interaction) simulations in the analysis of the fluid-mechanics of heart valves is becoming more and more important, being able to capture the interaction between the blood and both the surrounding biological tissues and the valve itself.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
